Efficiency and effectiveness metrics are two primary types of metrics. Efficiency IT metrics measure the performance of the IT system itself including throughput, speed, and availability. Effectiveness IT metrics measure the impact IT has on business processes and activities including customer satisfaction, conversion rate, and sell-through increase.
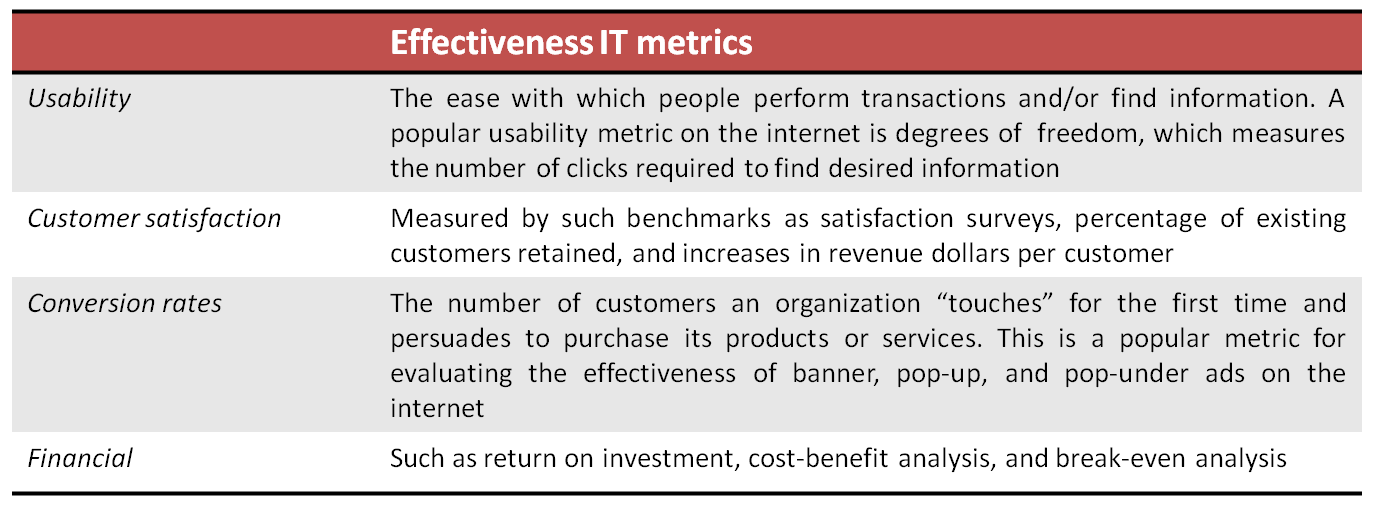
Effectiveness IT Metrics
Efficiency IT Metrics
METRICS FOR STRATEGIC INITIATIVE
Different financial ratios are used to evaluate a company's performance. companies can get additional insight into their performance by comparing financial ratios against other companies in their industry. A few of the more common financial ratios include:
- Internal rate of return ( IRR ) - the rate at which the net present value of an investment equals zero.
- Return on investment ( ROI ) - indicate the earning power of the project and is measured by dividing the benefit of a project by the investment.
- Payback method - numbers of years to recoup the cost of an initiative based on project annual net cash flow.
- Break-even analysis - determines the volume of business required to make a profit at the current price charged for the products or services.
Most managers are familiar with financial but unfamiliar with information system metrics. The following metrics will hape managers measure and manage their strategic initiatives:
- Website metrics
- Supply chain management ( SCM ) metrics
- Customer relationship management ( CRM ) metrics
- Business process reengineering ( BPR ) metrics
- Enterprise resource planning ( ERP ) metrics
WEBSITE METRICS
- Abandoned registrations : Number of visitor who start the process of completing a registeration page and then abandon the activity.
- Abandoned shopping carts : Number of visitor who create a shopping cart and start shopping and then abandon the activity before paying for the merchandise.
- Click-through : Count of the number of people who visit a site, click on and ad, and are taken to the side of the advertiser.
- Conversion rate : Percentage of potential customer who visit a site and actually buy something.
- Cost-per-thousand ( CPM ) : Sales dollars generated per dollar of advertising. This is commonly used to make the case for spending money to appear on a search engine.
- Page exposure : Average number of a page exposure to an individual visitor.
- Total hits : Number of visits to a website, many of which may be by the same visitor.
- Unique visitor : Number of unique visitor to a site in a given time. This is a commonly used by Nielsen/Net ratings to rankthe most popular website.
Balance scorecard is a management system, in addition to a measurement system, that enables organizations to clarify their vision and strategy and translate them into action. It provide feedback around both the internal business process and external outcomes in order to continuously improve strategic performance and result.
The balance scorecard views the organization from 4 perspective, and users should develop metrics, collect data, and analyze their business relative to each of this perspective:
- The learning and growth perspective
- The internal business process perspective
- The customer perspective
- The financial perspective
.png)










